[Summary: Online social networks have a role to play in bridging one off engagement with more structured forms of participation.]
A bit of scene setting
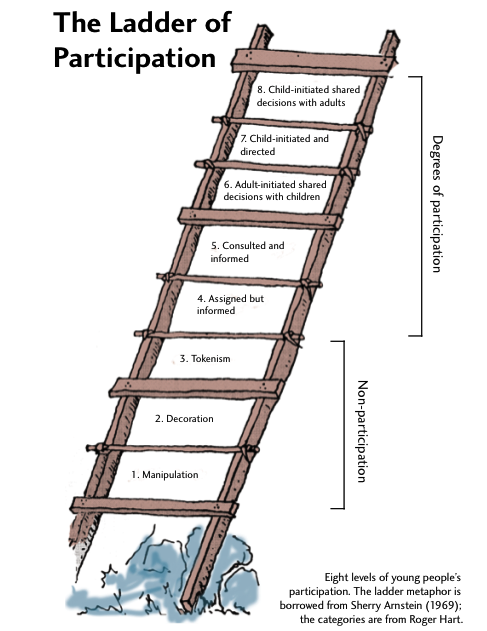
The ‘Ladder of Participation’ which asks organisations to consider the depth of youth participation in particular activities will be familiar to many people in youth engagement. Using Hart’s Ladder of Participation you can assess whether a youth council is acting as a genuine structure for youth empowerment, leading to young people and adults sharing decisions and creating change – or whether it is really a tokenistic gesture, creating the illusion of participation whilst adults are actually running the whole show.
But youth participation is not just about youth councils and young mayors. Good youth participation offers young people the chance to get involved and influence issues that affect them in a wide variety of ways, from one-off input into feedback and complaints processes, through to more structured engagement in the governance of organisations. On it’s own the ladder of Participation doesn’t show the full picture. That’s where the ‘matrix of participation’ comes in.
It’s a tool I’ve been using in training sessions for years, having first discovered in whilst working with Bill Badham delivering Hear by Right training. However, as far as I can tell we’ve never written it up online (though it is written up in this book which you can search inside with an Amazon account (search for ‘matrix’)).
The matrix of participation includes Hart’s Ladder of Participation on it’s vertical axis, and adds a horizontal axis consisting of different participation approaches, running roughly from one-off, short term or informal approaches on the left, to more structured and long-term approaches on the right.
Organisations can map the different participation opportunities they provide against both their level of participativeness, and against the type of approach they represent.
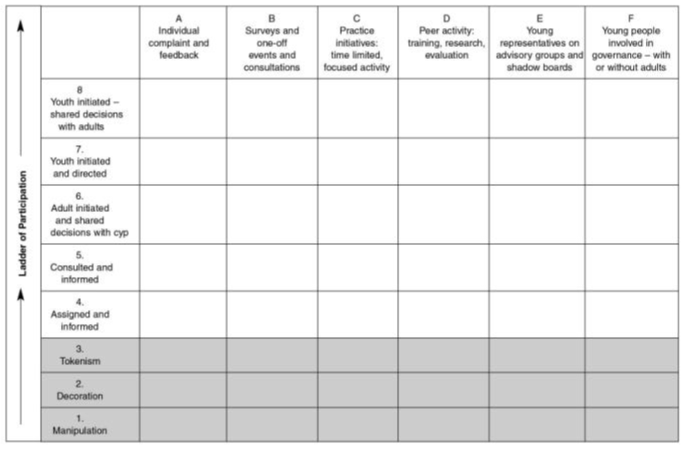
The matrix is particularly useful to encourage organisations to consider whether they are offering young people a spread of engagement opportunities, and our experience is that attempts to just provide opportunities at one side or other of the matrix is unlikely to lead to sustainable and effective youth participation which leads to positive change for young people.
An observation: the gap in the middle
When Bill Badham joined us at the April meeting of the Youth Participation and Social Network Sites Action Learning Set he led the group in using the matrix of participation (plus some post-it notes and a big sticky sheet) to put together a big visual representation of the different participation approaches in use amongst the 20 or so local authorities participating in the learning set.
Standing back from the wall where this matrix had been put together during the lunch break we spotted something interesting. The participation methods shown were clustered on the left and right of the matrix, and things were thin in the middle.

Already participants had been talking about how many of the more structured participation methods to the right were limited in their efficacy because they only managed to attract certain groups of young people who did not reflect the diversity of the young people the organisations worked with. And this got us thinking.
Participation methods towards the middle of the matrix are really important. It is through involvement in events; in creative projects; and in short-term activities that many young people can develop the confidence to express their views and can build the networks with other young people and with supportive adults that enable and encourage them to then get involved in further participation. The middle of the matrix is a key point on young people’s ‘pathway of participation’. Without opportunities to gain experience, information and develop networks – many young people (and often the young people we most need to hear from) may never go on to speak up in forums where they could have power to make serious change happen.
Bridging the gap: online social networks
Online social networking is not a cure all. But it seems that it could have a role to play here.
Right now, young people engaging in participation on the left of the matrix of participation, in one-off participation opportunities have few ways of connecting this engagement to longer term involvement in participation. Filling in a paper form to provide feedback on an activity and handing it in can often feel like a participation dead end.
But what if, instead of just handing in feedback, young people were encouraged to digitally provide their ideas for improvements to a service, and were to vote for the ideas supplied by other young people (see tools like UserVoice)?
And what if young people taking part in survey and small-scale engagement were offered an opt-in opportunity to connect with the person who will take forward action based on their input, so they can continue to engage with further questions that crop up as a policy or practice comes to be implemented?
And what if young people who want to express their view on a single issue could do that by joining a group within a social network, in the process coming to discover the other issues their peers are working on – and becoming part of a shared network with young people already involved in formal participation structures?
Not all young people will go on to ‘leap the gap’ themselves and move from one-off engagement to sitting on a youth forum or governance board (nor should they), but perhaps some will – and perhaps, equally importantly, those young people who take part in formal participation structures will have ways of keeping connected with the issues that matter to their least advantaged peers, and will be better able to represent the views of others and to advocate for improvements that benefit those most in need of change.
How are you blending online and offline social networks into your youth participation practice?
